DEFINITION: The blockchain interoperability drawback is the lack of blockchain networks to share knowledge, switch tokens (i.e., bridge), and carry out transactions with each other.
The fact of Web3 is multi-chain, the place a whole bunch to finally hundreds of various blockchains co-exist, every with totally different asset issuers, consumer bases, purposes, and technological strengths and weaknesses. The multi-chain strategy has overtaken the one unified ledger concept as a result of it’s extra scalable, versatile, and sensible given the wide selection of applied sciences, stakeholders, and pursuits concerned.
Nonetheless, for a multi-chain financial system to work, blockchains should be capable of seamlessly talk and switch belongings cross-chain in a safe and dependable method. Sadly, blockchain interoperability is a difficult drawback to resolve, with over $2.8B in consumer funds already hacked as a result of insecure cross-chain token bridges and infrastructure.
The next weblog will discover blockchain interoperability, its major challenges, and the way the Chainlink Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) units a brand new business commonplace in safety and strikes the business nearer to realizing the final word purpose of onchain changing into a single Web of Contracts.
What Is Blockchain Interoperability?
Blockchain interoperability is the flexibility of various blockchain networks to speak with each other by sending and receiving messages and tokens. Similar to the Web allows communication between computer systems, blockchain interoperability allows the cross-chain switch of knowledge and worth.
With out blockchain interoperability, blockchains are akin to digital islands the place their customers, belongings, and data are disconnected from the broader Web3 ecosystem. Thus, establishing a blockchain interoperability commonplace is important to unlocking the total potential of blockchain know-how as a result of it allows an interconnected onchain financial system that maximizes liquidity, offers common entry to customers, and realizes larger efficiencies and cross-chain collaboration. To study extra, try the weblog: What’s Blockchain Interoperability?
Key Challenges to Blockchain Interoperability
Know-how
As a result of method they generate consensus, blockchains are usually not designed to straight validate the state of all different onchain networks or offchain methods that exist on the planet with out introducing important compromises to the chain’s safety, stability, or scalability. This connectivity limitation is the premise of each the oracle drawback and the blockchain interoperability drawback.
Due to this fact, a blockchain interoperability resolution should be capable of learn and write knowledge in numerous codecs and interpret totally different consensus mechanisms to find out necessary info, equivalent to whether or not a transaction is taken into account finalized on a particular blockchain (i.e., transaction finality). It should even have its personal method of receiving, validating, and executing cross-chain transactions.
Performance
There are a number of functionalities {that a} blockchain interoperability resolution could also be requested to satisfy, most notably the flexibility to relay messages to/from totally different blockchains and switch tokens cross-chain utilizing a wide range of token dealing with mechanisms. Past that, there are different necessary functionalities {that a} blockchain interoperability resolution ought to ideally assist, equivalent to programmable token transfers—the flexibility to switch tokens cross-chain after which use these tokens in a supplementary motion on the vacation spot blockchain, all inside a single transaction. For instance, switch an asset cross-chain and deposit it in a staking contract as a part of the cross-chain transaction.
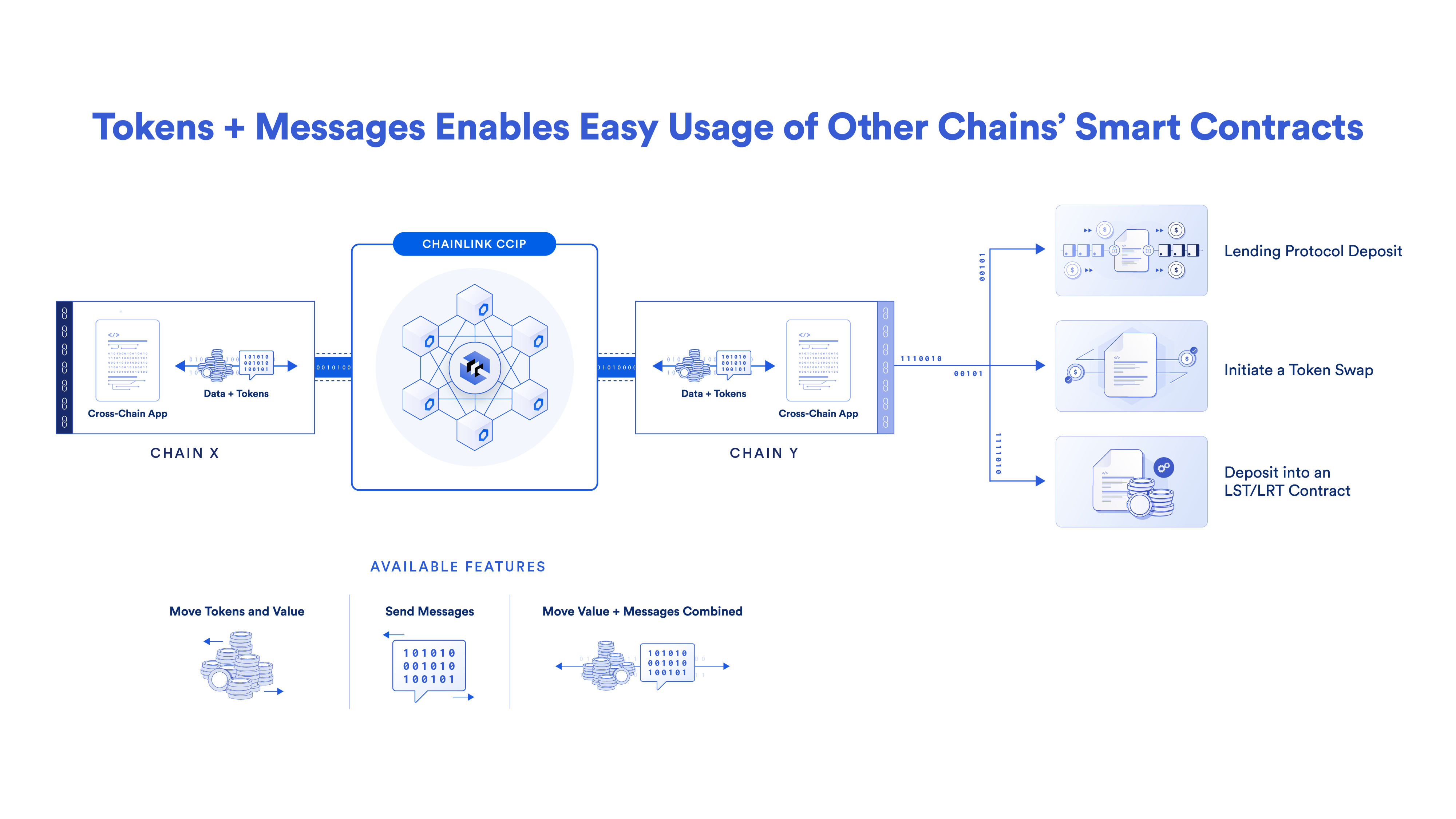
A blockchain interoperability resolution must also assist knowledge oracles as a method to set off automated cross-chain transactions based mostly on real-world or different blockchain occasions. Moreover, institutional shoppers might want further functionalities, equivalent to the flexibility to program varied organizational and compliance insurance policies into their cross-chain workflows or the flexibility to conduct privacy-preserving cross-chain transactions.
Safety
Validation of knowledge and transactions is essential to stopping a cross-chain protocol from being exploited. One of many major safety challenges stems from blockchains having totally different notions of transaction finality—the purpose at which previous blockchain transactions are deemed extraordinarily tough or not possible to revert. As such, a blockchain interoperability resolution wants to know the variations in blockchain design to make sure ample time has elapsed for finality on the supply blockchain earlier than taking motion on the vacation spot chain.
One other key notion of safety is how the blockchain interoperability resolution validates transactions or knowledge on the supply blockchain and relays the info to the vacation spot chain. These strategies embody centralized validation (e.g., a cryptocurrency change), native validation (e.g., atomic swap), native validation (e.g., zero-knowledge proof), or exterior validation (e.g., decentralized consensus). Totally different safety approaches include totally different trade-offs. For instance, extremely decentralized protocols might supply sturdy censorship resistance on the expense of developer flexibility and catastrophe restoration, whereas extra centralized protocols might supply the reverse.
Lastly, it’s necessary from a safety perspective to judge the onchain and offchain code of the protocol and the way battle-tested it’s when it comes to present process safety audits and operating securely in manufacturing. Moreover, their non-public key safety is of utmost significance—as compromised non-public keys are an assault vector usually exploited inside cross-chain options.
Standardization
Just like how TCP/IP creates a single commonplace for the World Extensive Internet, blockchains want a single commonplace to allow communication between them. By having a single commonplace in comparison with a mixture of totally different interoperability options with various ranges of safety ensures, liquidity can turn out to be unified throughout chains whereas safety requirements and workflows turn out to be standardized throughout use circumstances.
Chainlink’s Position in Blockchain Interoperability
CCIP (Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol) is a blockchain interoperability resolution powered by Chainlink. It’s particularly designed to deal with the numerous challenges of blockchain interoperability.
CCIP is an arbitrary messaging cross-chain protocol that may learn and write knowledge from any public or non-public blockchain, in addition to carry out a wide range of different functionalities for cross-chain transactions, equivalent to enabling token transfers by way of a wide range of token dealing with mechanisms (e.g., lock and mint, burn and mint, lock and unlock) and permitting customers to execute programmable token transfers. Moreover, CCIP is a part of a wider Chainlink platform that permits customers and establishments to get further companies wanted to facilitate cross-chain transactions, equivalent to Internet Asset Worth (NAV) knowledge, proof of reserves, pricing info, blockchain abstraction options, and extra.
Chainlink CCIP is the one blockchain interoperability resolution to succeed in level-5 cross-chain safety, and is powered by the identical decentralized consensus that has helped the Chainlink protocol allow over $12T in onchain transaction worth. It’s additionally the one blockchain interoperability protocol to characteristic an unbiased Danger Administration Community—a separate decentralized community that serves as a secondary validation and anomaly detection layer. You’ll be able to study extra in regards to the 5 ranges of cross-chain safety within the video under.
CCIP is already getting used throughout main DeFi protocols, equivalent to Aave’s stablecoin GHO, and among the world’s main monetary establishments, equivalent to DTCC, ANZ, and Swift. The flexibility to securely assist each DeFi and TradFi is important to establishing a regular that helps the subsequent period of digital finance based mostly on tokenized belongings and programmable cash and finance companies. There are additionally token bridges constructed on CCIP that present consumer interfaces for customers to switch tokens and messages throughout blockchains by way of CCIP. Two CCIP-powered interfaces embody Transporter and XSwap.
To study extra about Chainlink, go to chain.hyperlink, subscribe to the Chainlink publication, and observe Chainlink on Twitter, YouTube, and Reddit.










