Chainlink’s Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol helps liquid staking and restaking protocols scale by enabling them to permit their customers to stake their ETH immediately from layer-2 networks—considerably increasing the accessibility of liquid staking tokens (LSTs) and liquid restaking tokens (LRTs) throughout the multi-chain ecosystem. This functionality is uniquely enabled by CCIP’s help for Programmable Token Transfers, which allow the simultaneous switch of tokens and knowledge directions cross-chain.
Lido, a number one liquid staking protocol, not too long ago built-in CCIP to energy the brand new Lido Direct Staking rails, which allow customers to stake their ETH immediately from different blockchain networks and obtain wstETH, beginning with help for Arbitrum, Base, and Optimism. The brand new Lido Direct Staking rails are being adopted by numerous DeFi frontends together with XSwap, OpenOcean, and Interport.
Along with Lido, a rising variety of protocols are additionally integrating Chainlink CCIP to go cross-chain and allow the staking/restaking of ETH from layer-2 networks:
On this weblog, we’ll dive into the totally different ways in which CCIP can allow the staking of layer-1 property from layer-2 networks and the advantages this will deliver to the LST/LRT ecosystem.
Unlocking The Multi-Chain Demand for LSTs/LRTs
Liquid staking has turn into one of many largest sectors in DeFi, with over $40 billion in TVL. Restaking, and by extension liquid restaking, have additionally grown at an accelerated fee, with restaking representing roughly $13.7 billion in TVL (of which $10 billion is in liquid restaking kind).
Regardless of this development, a key limitation dealing with each liquid staking and restaking protocols is the liquidity and availability of their respective LSTs / LRTs throughout the multi-chain ecosystem. Whereas many such protocols have made their respective LST/LRT tokens bridgeable throughout various blockchains (in lots of instances through CCIP), the minting of latest LST/LRT tokens is commonly restricted to a single blockchain the place the core (re)staking protocol contracts function.
In consequence, it’s typically tough for holders of layer-1 property on layer-2 networks to mint LST/LRT tokens. For instance, holders of ETH on layer-2 networks seeking to (re)stake their ETH should manually bridge their ETH again to Ethereum mainnet (which can take as much as 7 days with optimistic rollups), stake their ETH in change for his or her LST/LRT of alternative, after which manually bridge their LST/LRT again to the layer-2 community.
Chainlink CCIP and its help for Programmable Token Transfers might help compress all of those steps right into a single layer-2 transaction from the person’s perspective.
How CCIP Allows Cross-Chain Connections To Liquid Staking and Restaking Protocols
CCIP Programmable Token Transfers allow sensible contracts to switch tokens cross-chain together with knowledge directions on what the receiving sensible contract ought to do with these tokens as soon as they arrive on the vacation spot chain. This programmability is vital to enabling advanced cross-chain interactions, equivalent to cross-chain staking, because it allows customers on one blockchain to work together with and profit from sensible contracts on one other blockchain—with out ever leaving their most popular blockchain setting.
A staking protocol’s use of CCIP to allow (re)staking from layer-2 networks could be achieved in a number of other ways, relying on the velocity and value preferences of the (re)staking protocol and its customers.
Direct Method
The way it works on Ethereum: Within the direct method, an end-user initiates a staking interplay on a layer-2 community, after which their ETH, together with knowledge directions on what to do with the tokens, are despatched to Ethereum through CCIP. A receiving sensible contract on Ethereum receives the ETH, stakes it right into a liquid (re)staking protocol, and the newly minted LSTs/LRTs representing that staked place are then bridged again to the person’s pockets deal with on the layer-2.
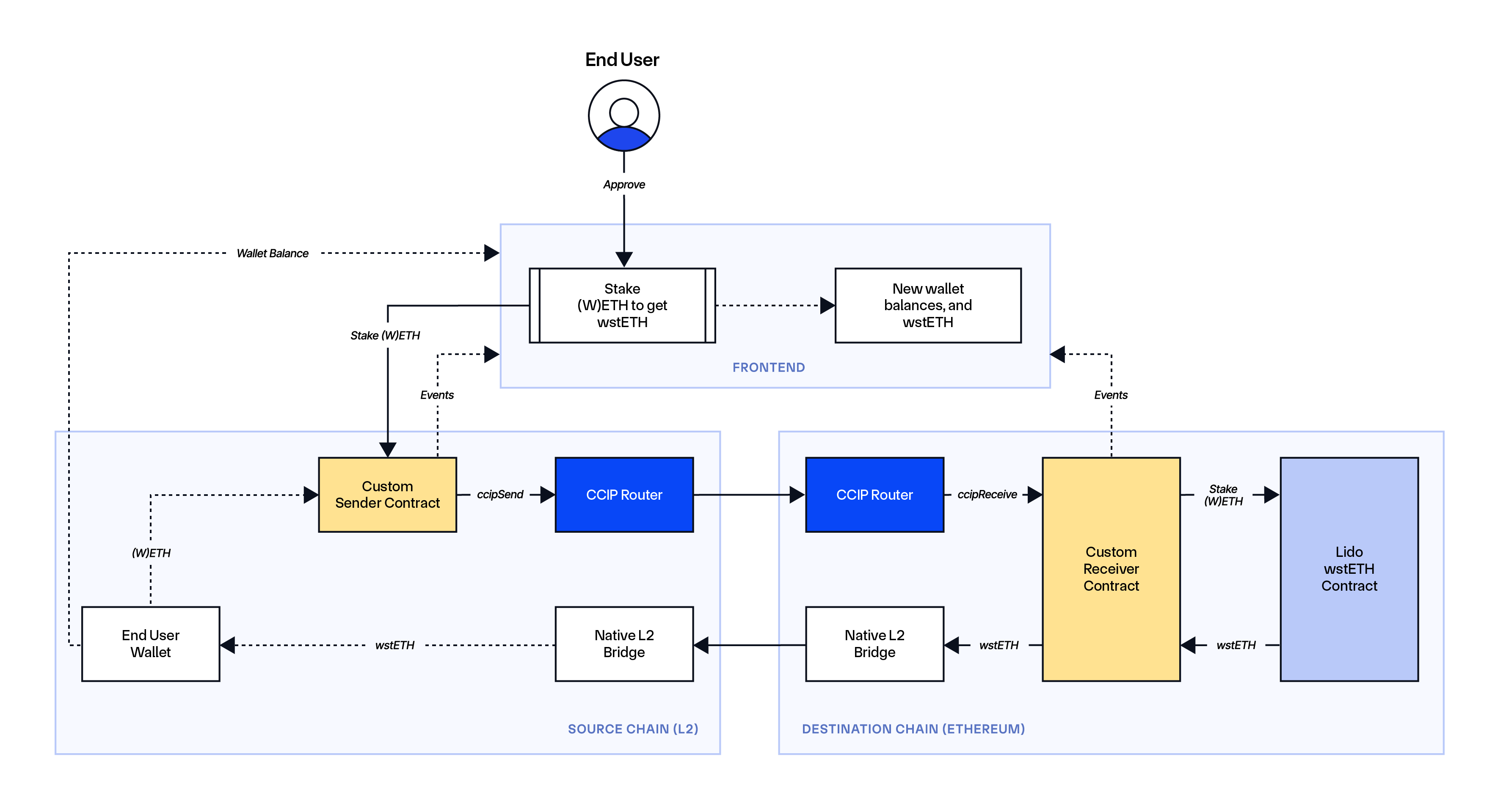
Advantages/Challenges: This method is very cost-effective for (re)staking protocols to help because it includes no liquidity administration operations, however customers should wait till all cross-chain transactions concerned within the course of have been accomplished with a purpose to obtain their LST/LRT tokens on the layer-2 community (customers obtain their LST/LRT in a separate transaction later in time asynchronously).
Examples:
Lido’s Direct Staking rails use CCIP to help the direct staking technique of staking ETH for wstETH from layer-2 networks, along with the liquidity pool method.
EigenPie is integrating CCIP to allow its customers to restake ETH for egETH from layer-2 networks.
StakeStone is integrating CCIP to allow its customers to stake ETH for STONE from layer-2 networks.
Liquidity Pool Method
The way it works on Ethereum: Within the liquidity pool method, an end-user initiates a staking interplay on a layer-2 community and instantly receives an LST/LRT from the (re)staking protocol’s liquidity pool. That is achieved through the use of an change fee knowledge feed to report the (re)staking protocol’s inside change fee for the LST/LRT on that L2 or through the use of CCIP to bridge the change fee knowledge. As soon as the ETH deposited by the person into the (re)staking protocol’s liquidity pool is shipped to Ethereum through CCIP together with the directions for the receiving sensible contract to (re)stake, the newly minted LST/LRT is then bridged again to layer 2 to replenish the liquidity pool.
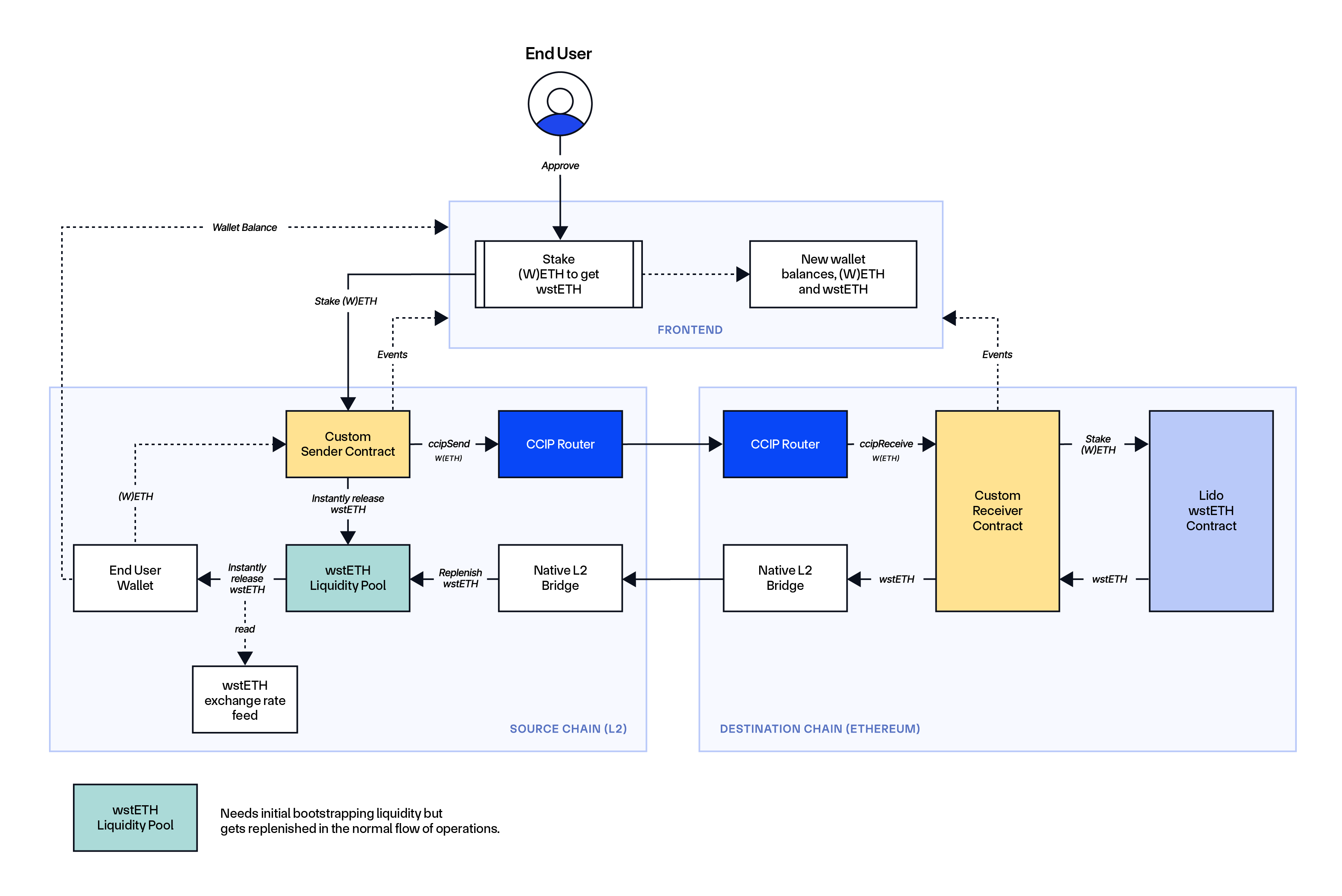
Chainlink Automation can be utilized to allow transaction batching, the place after a specific amount of ETH is collected within the liquidity pool (or a sure period of time has handed), CCIP is triggered to switch a batch of ETH to Ethereum the place a receiving sensible contract can (re)stake that ETH into an LST/LRT format and bridged again to the layer-2 to replenish the liquidity pool, lowering the liquidity administration prices for the (re)staking protocol.
Advantages/Challenges: This technique allows customers to immediately obtain LSTs / LRTs throughout the similar atomic transaction they provoke a staking interplay, however requires (re)staking protocols to bootstrap a liquidity pool—which might turn into self-sustaining by the replenishing course of. For this method, the (re)staking protocol should handle liquidity for its LST/LRT on the layer-2 networks the place the characteristic is made accessible. If a person makes an attempt to stake a considerable amount of ETH, there must be sufficient accessible liquidity within the pool or in any other case present a fallback to the direct method of utilizing CCIP to stake from layer-2 networks.
Examples:
Lido’s Direct Staking rails use CCIP to help the liquidity pool technique of staking ETH for wstETH from layer-2 networks, along with supporting the direct method.
Frax is integrating CCIP to allow its customers to stake ETH for sfrxETH from layer-2 networks. If liquidity within the layer-2 liquidity pool is inadequate to cowl a staking transaction, Frax will even help the direct staking method with CCIP.
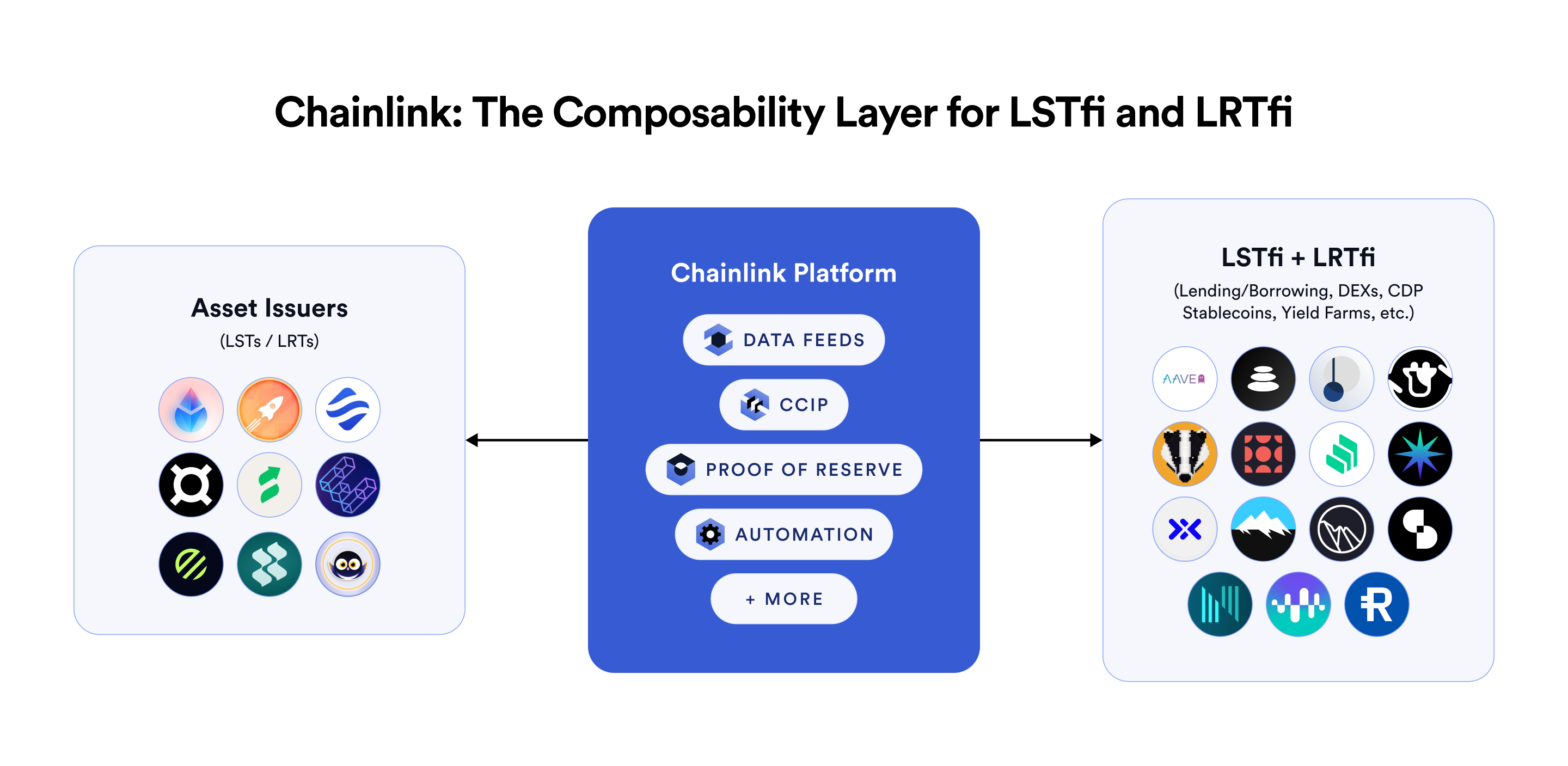
The Chainlink Platform For Liquid Staking and Restaking Protocols
CCIP affords builders flexibility to energy all variations of cross-chain (re)staking for LST/LRT protocols. Notably, these capabilities are powered by the Chainlink platform, which allows superior performance by the mix of industry-standard providers, and with little-to-no further belief assumptions when utilizing a number of providers:
CCIP unlocks programmable token transfers that allow worth and messages to be despatched inside a single transaction.
Information Feeds relay the inner redemption charges for LSTs/LRTs throughout chains.
Proof of Reserve verifies the reserves backing LSTs/LRTs.
Automation helps dependable liquidity pool rebalancing operations.
You possibly can learn extra about Chainlink’s help for the staking and restaking ecosystems in How the Chainlink Platform Unlocks LST and LRT Adoption in DeFi. For a deeper technical dive, take a look at CCIP Masterclass: Cross-Chain Staking Version.
If you’re a DeFi protocol or conventional monetary establishment and wish to discover how CCIP Programmable Token Transfers can unlock your cross-chain and tokenization use instances, attain out to our staff of specialists. If you’re a developer and wish to get began with CCIP Programmable Token Transfers, take a look at the Chainlink documentation for extra technical assets.
Disclaimer: This submit is for informational functions solely and incorporates statements concerning the future, together with anticipated product options, improvement, and timelines for the rollout of those options. These statements are solely predictions and mirror present beliefs and expectations with respect to future occasions; they’re primarily based on assumptions and are topic to danger, uncertainties, and modifications at any time. There could be no assurance that precise outcomes won’t differ materially from these expressed in these statements, though we imagine them to be primarily based on cheap assumptions. All statements are legitimate solely as of the date first posted. These statements could not mirror future developments because of person suggestions or later occasions and we could not replace this submit in response. Please overview the Chainlink Phrases of Service, which gives essential data and disclosures.










